About Webhooks
- Introduction
- Accessing Webhook Management
- Creating a Webhook
- Managing Webhooks
- Viewing Execution Logs
- Testing Webhooks
- Webhook Configuration Options
- Security: HMAC Signatures
- Custom Headers
- Retry Logic
- Webhook Payload Examples
- Troubleshooting
- Using Logs for Debugging
- Best Practices
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction
The Webhook Management feature allows you to receive real-time notifications when specific events occur in your ILC/PT and Intra workflows. Instead of manually checking the system, webhooks automatically send data to your specified endpoint whenever an event happens.
What are Webhooks? Webhooks are HTTP callbacks that send data to your server when events occur. Think of them as “reverse APIs” – instead of you asking for data, the system pushes data to you automatically.
Accessing Webhook Management
- Log in to the NAPT Customer Portal
- Navigate to Settings from the main menu
- Click on Webhook Management (admin access required)
Note: Only users with admin privileges can access and manage webhooks.
Overview
The Webhook Management page has two main sections:
- Webhooks Tab: Manage your webhook configurations
- Execution Logs Tab: View webhook execution history and details
Creating a Webhook
Step 1: Open the Add Webhook Dialog
From the Webhooks tab, click the “Add Webhook” button. A modal dialog will open for webhook configuration.
Step 2: Configure Basic Information
Name (Required)
- Enter a descriptive name for your webhook
- Example: “ILC Order Notifications”
- This helps you identify the webhook later
Event Type (Required)
- Select the event that should trigger this webhook
- Available options:
- ILC/PT Order: Triggered when an ILC/PT order is placed
- More event types will be available in future updates
- ILC/PT Order: Triggered when an ILC/PT order is placed
- More event types will be available in future updates
Step 3: Configure HTTP Settings
HTTP Method (Required)
- Choose how your endpoint receives data:
- POST: Payload sent as JSON in request body (recommended)
- PUT: Payload sent as JSON in request body
- GET: Payload sent as URL-encoded query parameters
- POST: Payload sent as JSON in request body (recommended)
- PUT: Payload sent as JSON in request body
- GET: Payload sent as URL-encoded query parameters
- Default: POST
Webhook URL (Required)
- Enter the full HTTPS URL where webhooks should be sent
- Example:
https://your-server.com/api/webhooks/ilc-order - Must be a valid HTTPS URL
Important Notes:
- POST/PUT: Payload is sent as JSON in the request body
- GET: Payload is sent as URL-encoded query parameters
- Test: The test button will send a sample payload matching the selected event type structure
Step 4: Configure Advanced Options
Secret (Optional)
- Enter a secret key for HMAC signature verification
- If provided, webhooks will include an
X-Webhook-Signatureheader - Use this to verify webhook authenticity on your server
Retry Count
- Maximum number of retry attempts if webhook fails
- Default: 3
- Range: 1-10
Timeout (seconds)
- HTTP request timeout in seconds
- Default: 30
- Range: 5-120
Custom Headers (Optional)
- Add custom HTTP headers as JSON
- Example:
{"Authorization": "Bearer your-token", "X-Custom-Header": "value"} - Useful for authentication or custom routing
Step 5: Set Active Status
Active Toggle
- Enable or disable the webhook
- Inactive webhooks won’t be triggered
- Default: Enabled
Step 6: Test Your Webhook (Recommended)
- Click “Test Webhook” to send a sample payload
- This helps verify your endpoint is working correctly
- The test uses a sample payload matching your selected event type
Step 7: Save the Webhook
- Click “Save” to create the webhook
- The webhook will appear in your webhooks list
- It will be active immediately if enabled
Managing Webhooks
Viewing Your Webhooks
The Webhooks tab displays all configured webhooks in a table with the following columns:
- Name: Webhook identifier
- Event Type: Event that triggers the webhook
- Method: HTTP method (GET, POST, or PUT)
- Active: Current status (enabled/disabled)
Editing a Webhook
- Click the “Manage” button next to the webhook
- The edit modal opens with current configuration
- Modify any settings as needed
- Click “Test Webhook” to verify changes (optional)
- Click “Save” to update
Enabling/Disabling Webhooks
- Quick Toggle: Use the Active column toggle to enable/disable without opening the edit modal
- Via Edit Modal: Change the Active toggle in the edit form
Note: Disabled webhooks remain in the system but won’t be triggered by events.
Deleting a Webhook
- Click the delete icon (trash can) next to the webhook
- Confirm the deletion in the dialog
- The webhook will be permanently removed
Warning: Deleting a webhook cannot be undone. Execution logs for deleted webhooks will remain in the system.
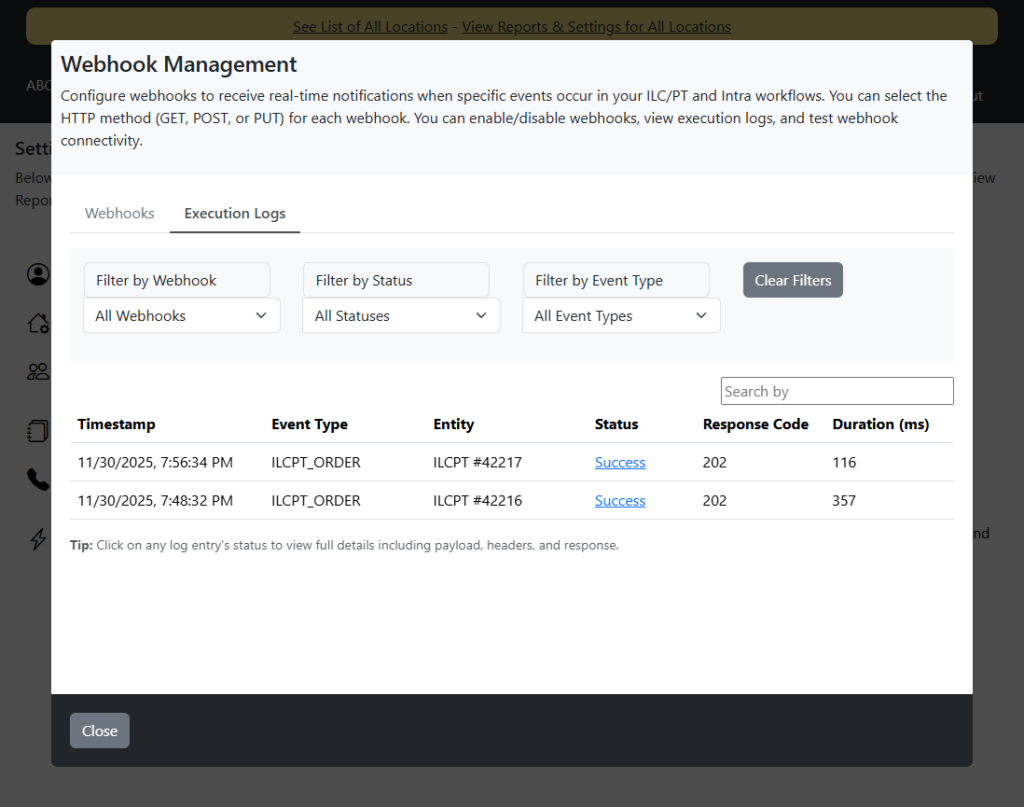
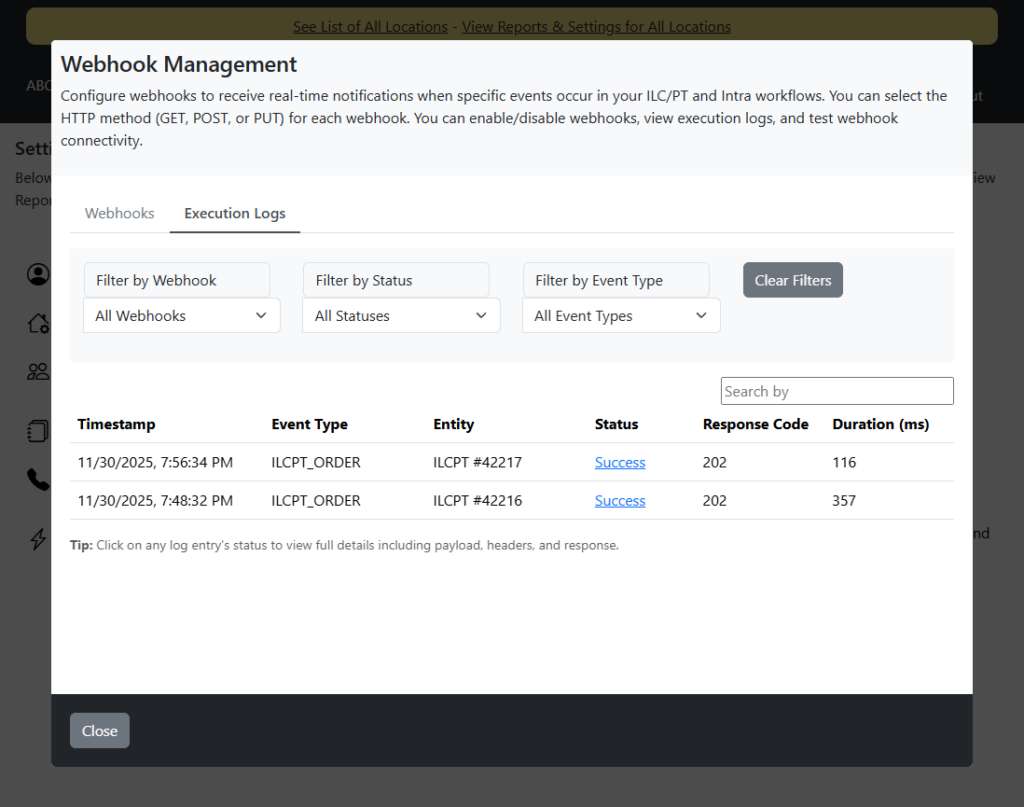
Viewing Execution Logs
The Execution Logs tab provides detailed information about all webhook execution attempts.
Accessing Logs
- Click the “Execution Logs” tab
- View the list of all webhook executions

Log Columns
The logs table displays:
- Timestamp: When the webhook was triggered
- Event Type: The event that triggered the webhook
- Entity: Entity type and ID (e.g., “ILCPT #12345”)
- Status: Execution status (Success, Failed, Pending, Retrying)
- Response Code: HTTP response code from your endpoint
- Duration (ms): How long the request took
Filtering Logs
Use the filter options at the top of the logs table:
- Filter by Webhook: Select a specific webhook to view only its logs
- Filter by Status: Filter by Success, Failed, Pending, or Retrying
- Filter by Event Type: Filter by specific event types
- Clear Filters: Reset all filters to show all logs
Viewing Log Details
- Click on the Status cell of any log entry
- A detailed modal opens showing:
- Request Information: URL, event type, entity, status, attempt number, timestamps
- Payload: Complete JSON payload that was sent
- Request Headers: All HTTP headers included in the request
- Response Body: Response received from your endpoint
- Error Message: Error details if the webhook failed
- Request Information: URL, event type, entity, status, attempt number, timestamps
- Payload: Complete JSON payload that was sent
- Request Headers: All HTTP headers included in the request
- Response Body: Response received from your endpoint
- Error Message: Error details if the webhook failed
Understanding Log Statuses
- Success: Webhook was delivered successfully (HTTP 200-299)
- Failed: Webhook delivery failed after all retry attempts
- Pending: Webhook is queued but not yet sent
- Retrying: Webhook failed but will be retried
Testing Webhooks
The test feature allows you to verify your webhook endpoint without waiting for a real event.
How to Test
While Creating/Editing:
- Fill in the webhook configuration
- Click “Test Webhook” button
- A sample payload matching your event type will be sent
- Fill in the webhook configuration
- Click “Test Webhook” button
- A sample payload matching your event type will be sent
Test Requirements:
- Webhook URL must be entered
- Event Type must be selected
- Your endpoint must be accessible
- Webhook URL must be entered
- Event Type must be selected
- Your endpoint must be accessible
Test Results
After testing, a modal displays:
- Response Code: HTTP status code from your endpoint
- Response: First 200 characters of the response body
- Success/Error Message: Whether the test was successful
Webhook Configuration Options
POST (Recommended)
- Payload Location: Request body as JSON
- Content-Type:
application/json - Use Case: Most common, best for complex data structures
PUT
- Payload Location: Request body as JSON
- Content-Type:
application/json - Use Case: Similar to POST, for idempotent operations
GET
- Payload Location: URL query parameters
- Content-Type: Not set
- Use Case: Simple integrations, webhooks that don’t accept POST
Security: HMAC Signatures
If you provide a Secret when creating a webhook, the system will include an HMAC-SHA256 signature in the X-Webhook-Signature header.
Header Format: X-Webhook-Signature: sha256=<signature>
Custom Headers
Custom headers allow you to:
- Add authentication tokens
- Include API keys
- Set custom identifiers
- Configure routing headers
Format: JSON object
Retry Logic
The system automatically retries failed webhooks:
- Retry Count: Configurable per webhook (default: 3)
- Retry Strategy: Exponential backoff
- Retryable Errors: Network errors, 5xx server errors, 429 (rate limit)
- Non-Retryable Errors: 4xx client errors (except 429)
Webhook Payload Examples
ILC/PT Order Event
Event Type: ILCPT_ORDER
Payload Structure:
{
"event": "ILCPT_ORDER",
"timestamp": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z",
"version": "1.0",
"data": {
"companyId": 100,
"companyName": "ABC Labs",
"orderedBy": {
"contactId": 25,
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@abclabs.com"
},
"orderDate": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z",
"items": [
{
"scheme": "Temperature Calibration",
"testIds": [12345, 12346, 12347]
},
{
"scheme": "Pressure Calibration",
"testIds": [12348, 12349]
}
]
}
}
Notes:
- This webhook fires once per order, not per individual ILC/PT
- The
itemsarray groups test IDs by scheme name - A single order can create multiple ILC/PTs across different schemes
Troubleshooting
Webhook Not Receiving Data
Check:
- Is the webhook Active? (Check the Active column)
- Is the URL correct and accessible?
- Check the Execution Logs for error messages
- Verify your endpoint accepts the configured HTTP method (POST/GET/PUT)
- Check if your server firewall allows incoming connections
Solution: Review the Execution Logs tab for specific error messages.
Webhook Failing with 4xx Errors
Common Causes:
- Invalid URL format
- Endpoint requires authentication (add Custom Headers)
- Endpoint doesn’t accept the HTTP method
- Payload format mismatch
Solution:
- Verify URL is correct
- Add authentication headers if needed
- Check endpoint documentation
- Review payload in Log Details
Webhook Timing Out
Symptoms: Logs show timeout errors, no response received
Causes:
- Server is slow to respond
- Network connectivity issues
- Endpoint is down
Solutions:
- Increase Timeout value (up to 120 seconds)
- Check server performance
- Verify endpoint is accessible
- Review network connectivity
HMAC Signature Verification Failing
Check:
- Secret matches between webhook config and your server
- You’re verifying the raw request body (not parsed JSON)
- Signature format is correct:
sha256=<hex>
Solution: Compare the signature in Request Headers (from Log Details) with your verification code.
Using Logs for Debugging
- Filter by Status: View only Failed webhooks
- Click Status: Open Log Details to see:
- Exact payload sent
- Headers included
- Error message
- Response from your endpoint
- Exact payload sent
- Headers included
- Error message
- Response from your endpoint
- Check Timestamps: Identify patterns or outages
- Review Response Codes: Understand failure types
Best Practices
Security
- Always Use HTTPS: Never configure webhooks with HTTP URLs
- Use HMAC Signatures: Enable secret verification for production webhooks
- Rotate Secrets: Periodically update webhook secrets
- Validate Payloads: Always verify webhook data on your server
- Use Custom Headers: Add authentication instead of relying on URL parameters
Reliability
- Set Appropriate Timeouts: Match your server’s response time
- Configure Retry Counts: Balance between reliability and avoiding spam
- Monitor Logs Regularly: Check Execution Logs weekly for issues
- Test Before Production: Use the Test feature before enabling webhooks
- Handle Idempotency: Design endpoints to handle duplicate webhooks
Performance
- Respond Quickly: Keep endpoint response time under 5 seconds
- Return 200 OK: Acknowledge receipt immediately, process asynchronously
- Avoid Blocking: Don’t perform long operations in webhook handler
- Use Queues: Process webhook data asynchronously on your server
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How many webhooks can I create?
A: There’s no hard limit, but we recommend keeping the number reasonable for easier management.
Q: Can I have multiple webhooks for the same event?
A: Yes! You can create multiple webhooks for the same event type, each pointing to different endpoints.
Q: What happens if my endpoint is down?
A: The system will retry according to your Retry Count setting. After all retries are exhausted, the webhook will be marked as Failed in the logs.
Q: Are webhooks sent in real-time?
A: Yes, webhooks are triggered immediately when events occur. There may be a small delay (seconds) for processing and delivery.
Q: Can I edit a webhook after it’s created?
A: Yes, you can edit any webhook configuration at any time. Changes take effect immediately.
Q: Do webhooks work for historical data?
A: No, webhooks only trigger for new events after they’re configured. They don’t retroactively send data for past events.
Q: What’s the difference between POST and GET methods?
A: POST sends data in the request body as JSON, while GET sends data as URL query parameters. POST is recommended for most use cases.
Q: How long are execution logs kept?
A: Execution logs are retained for 90 days. Older logs may be archived.
Q: What should I do if webhooks keep failing?
A:
- Check the Log Details for specific error messages
- Verify your endpoint is accessible and responding correctly
- Test the webhook using the Test feature
- Review your endpoint logs
- Contact support if issues persist
